Coin Highlight: Bitcoin (BTC)
 8 minutes
8 minutes

 8 minutes
8 minutes

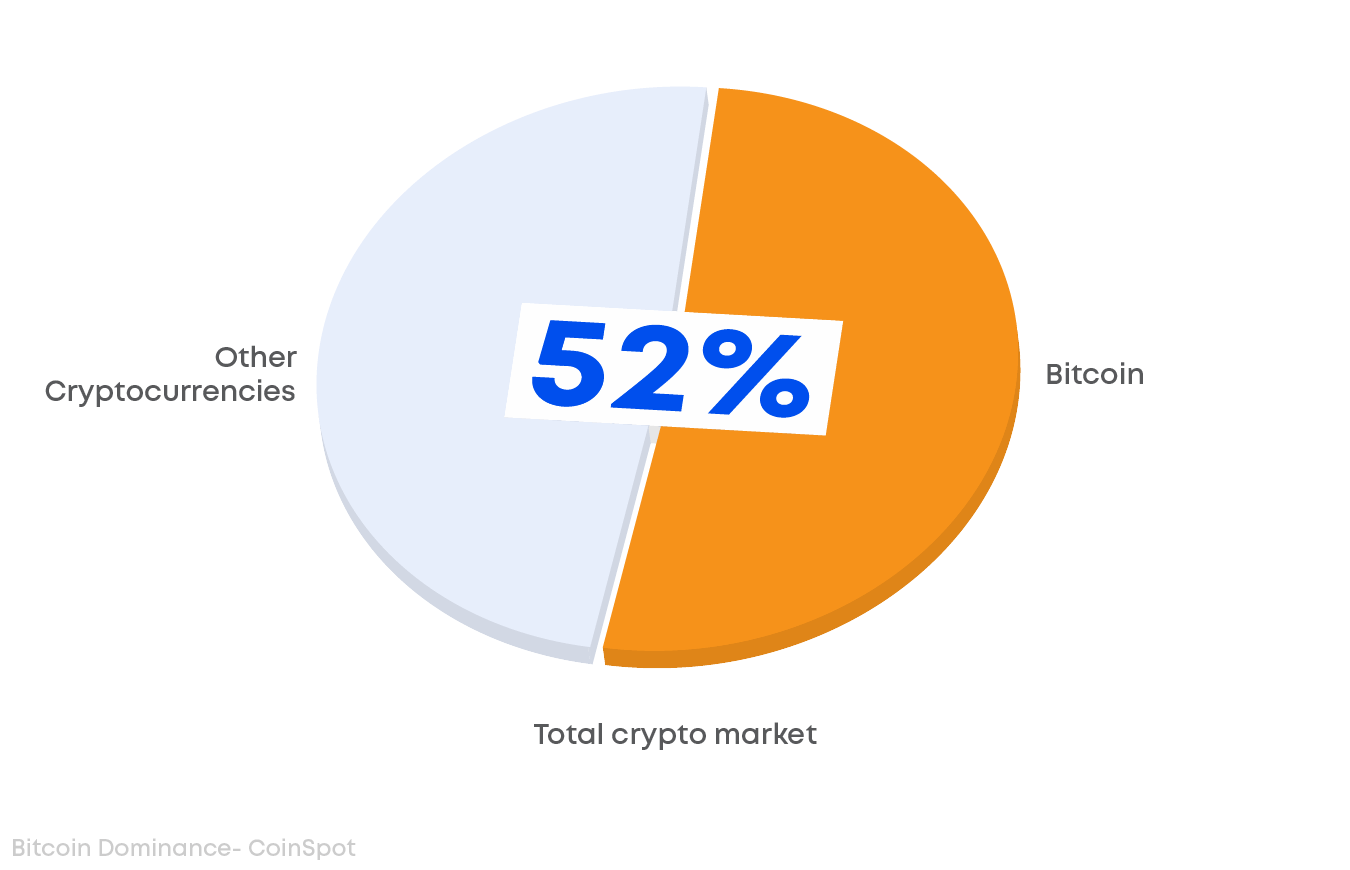
Bitcoin is the first ever cryptocurrency. Created in 2009, Bitcoin (BTC) has become the face of a growing and extremely influential industry. However, the general public is still largely unaware of Bitcoin and cryptocurrency as a whole, why it was created, and what it means for the wider economy. Since its launch, Bitcoin is still the highest performing cryptocurrency and dominates the market. In this article we will look at the history, purpose and function of Bitcoin, the world's most popular cryptocurrency.
Bitcoin was the first cryptocurrency and was created by the mysterious programer Saroshi Nakamoto in 2009. By the end of Bitcoin’s first year in the wild it was worth $0.0010 per BTC. It was not until 2012 that Bitcoin started its rise. And by 2015 a number of retailers began to accept Bitcoin as a form of payment. What made Bitcoin unique was its decentralised nature. By utilising its peer to peer payment system, Bitcoin transactions do not require an intermediary to approve or review transactions. A very novel concept in terms of a currency that can be used to buy and sell. At the same time the blockchain was an unexplored technological topic which was popularised by Bitcoin and its many use cases.
In 2016/2017 Bitcoin hit a major price milestone, going above the $1,000 dollar barrier. By 2020 Bitcoin was a household name, and its popularity continued to grow. It only continued to grow, reaching its all time high price in 2021 of $94,906 AUD. Since then Bitcoin has persisted and continued to be the number one cryptocurrency, dominating the industry.
Bitcoin’s main purpose is to operate as a decentralised global payment system. This means that people are able to send and receive funds locally or internationally, without needing to use a third party (such as a bank or payment provider). Bitcoin is often referred to as a ‘Store of Value’ like precious metals because it is scarce and hard to produce. The decision by the United States IRS continued to support this, in 2013 they began to treat BTC as a commodity instead. These characteristics are appealing to investors. However, Bitcoin continues to be used as a currency, being accepted by a number of different retailers. Innovations by CoinSpot such as the CoinSpot Mastercard continue to promote its practical use in this way. Some may argue Bitcoin’s main purpose is to pave the way for new cryptocurrencies and encouraging the innovation of blockchain technology in our world today. Showing the general public how versatile and useful this technology can be for a number of different industries.
There are a number of features that Bitcoin shares with other currencies, and ones unique to Bitcoin that make it so revolutionary. Firstly, its decentralised nature. Now this is not that unique among digital currencies, however at the time of Bitcoins creation it was a very novel concept. The decentralisation of the Bitcoin network acts as an independent check and balance system that does not depend on a middle man.
Interestingly enough, Bitcoin also has a hard cap of 21 Million coins. This means that there will never be more than 21 Million Bitcoin in circulation at once. This was done for a number of reasons. However arguably the most important one was its anti-inflationary nature. Although the number of Bitcoins will never likely reach 21 Million, the cap helps to ensure the virtual currency will continue to exist without traditional inflationary pressures.
Finally the freedom of peer-to-peer transactions. Asd a global currency, Bitcoin can be sent without issue or delay across the globe between individuals, and then exchange for the local currency if they so choose. This level of freedom, and lack of third party interference truly makes it the closest we have ever been to a universally accepted currency.
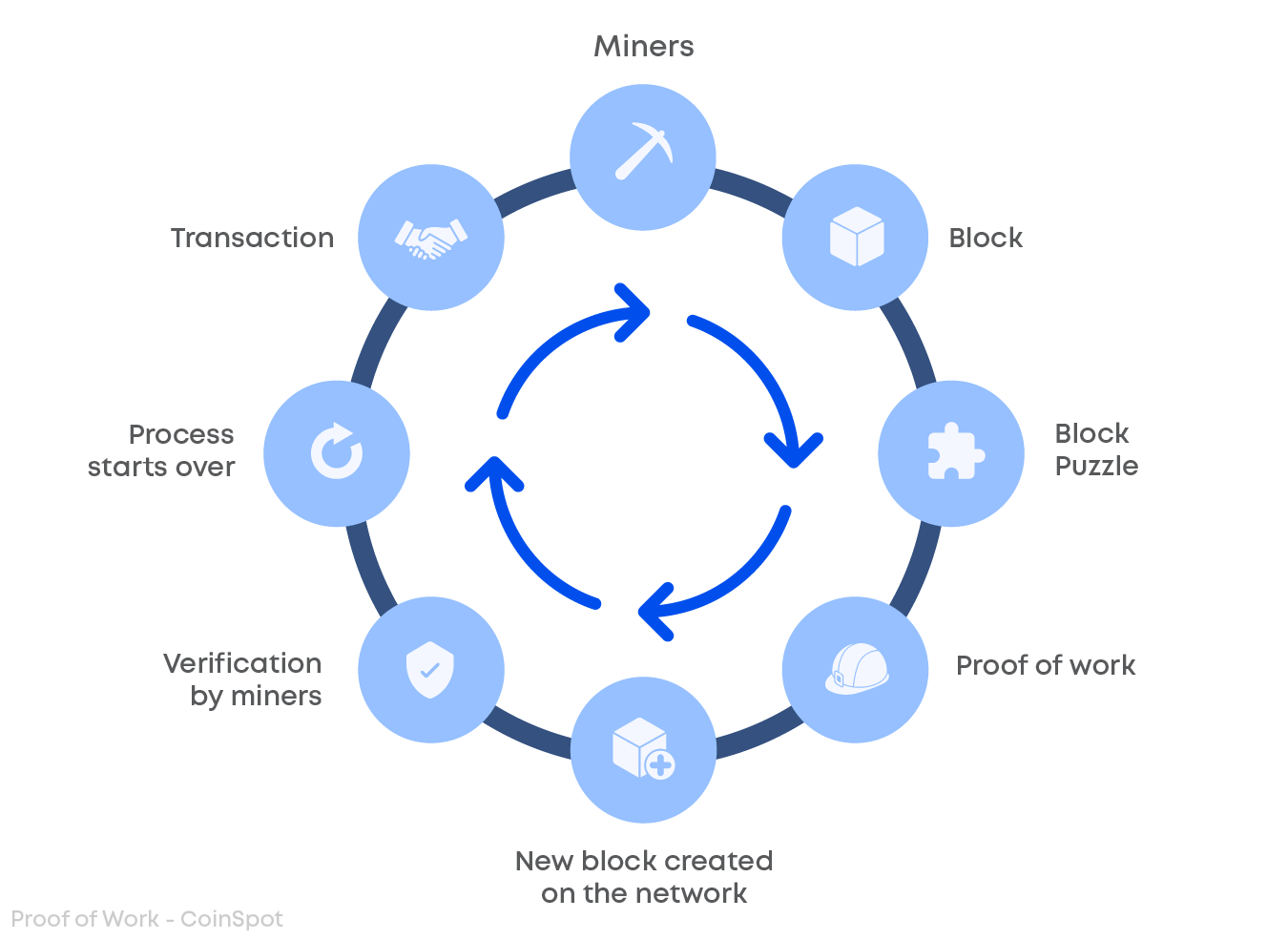
There are a number of key pieces of technology that, when working together, allow Bitcoin to function. The first and most important would be the blockchain. The Bitcoin blockchain utilises something called a Proof of Work consensus model. The data on the blockchain is not stored in a single place, but is distributed across multiple nodes, or computers, within the network. Every node in the network has a copy of the blockchain, and transactions are only validated when there is consensus from every node in the network. Miners help to validate these transactions and do so via specialised applications. Miners compete with one another to solve complicated math problems called hashes, the winner gets a Bitcoin reward and a new block is created. By utilising this system, the blockchain becomes an immutable ledger that is replicated between all nodes within the network. This means that no new blocks are created until all nodes in the network have achieved consensus.
To ensure that the cap of 21 million Bitcoin is maintained, every four years or so an event called the ‘Halving’ occurs. This is where the rewards miners receive for validating a block is cut in half. If the last Bitcoin is mined it is predicted to occur in 2140, after this the miners will be rewarded in network fees.
There are a number of viable practical applications for Bitcoin in today's society. One of the main appeals is cross border purchases. Without the need to transfer to different currencies, individuals can make peer-to-peer transfers without losing value due to exchange rates. This is a major change to traditional finance, where time of exchange can play a major role in the end price.
An example of Bitcoin being used as a currency currently is El Salvador, where the population has little access to intermediaries such as banks. Bitcoin provided a new means of payment for their country allowing quick peer to peer transactions without the need for traditional economic infrastructure.
The development and continued mainstream adoption of Bitcoin has only increased. One of the most recent major events to occur was the approval of the Bitcoin ETF. An ETF or exchange traded fund, is a financial product that tracks the price of an asset, or collection of assets, that can be bought and sold on a stock exchange. What makes this so significant is the fact the market was opened up to traditional investors.
The lightning network is also something that could improve the already robust features Bitcoin enjoys. The lightning network is a layer 2 protocol built on the Bitcoin Blockchain. It aims to speed up Bitcoin transactions while lowering the traditionally high energy costs associated with maintaining the Bitcoin blockchain. It is updates like this that will allow Bitcoin to maintain its position as the top cryptocurrency and will improve its overall utilisation.
If you’re wondering how to buy BTC? The easiest way to buy Bitcoin in Australia is through CoinSpot; Australia’s largest cryptocurrency platform. Once you have created a free account you will have access to your very own Bitcoin Wallet plus over 300 other cryptocurrencies and their corresponding wallets. Using CoinSpot you can instantly purchase Bitcoin and it will reflect into your wallet instantaneously. There are multiple ways you can purchase Bitcoin other than our Instant buy/sell; these options are the CoinSpot Markets, Over the Counter (OTC), Recurring Buy & Swap which allows you to directly trade Bitcoin with other cryptocurrencies.
